What is Wharton’s Jelly?
Wharton’s jelly is not a food spread you eat with peanut butter. It is a connective tissue that is a rich source of mesenchymal stem cells that have many applications in the field of regenerative medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are cells that can differentiate (transform) into bone cells, cartilage, muscles cells, skin cells, neural cells and corneal cells. More importantly, mesenchymal cells are signally cells that recruit other cells to initiate a healing response. Arthur Caplan, MD has suggested that MSCs be call medicinal signaling cells.
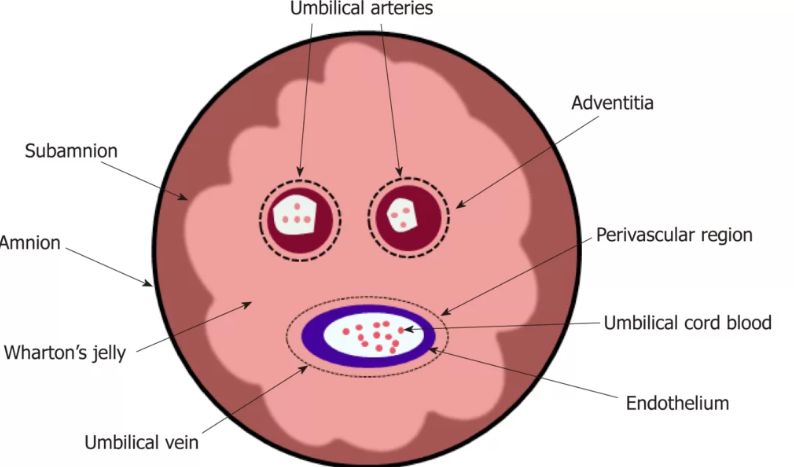
Where does Wharton’s jelly come from? It is a gelatin-like substance found in human umbilical cords. It is unique form of connective tissue in that it only consists of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In addition to the mesenchymal cells, Wharton’s jelly is high in collagen, hyaluronic acid, glcyprotein, plasma proteins, and chondroitin sulfate all of which are vital to healthy tissues.
Wharton’s jelly has a couple of interesting functions. The umbilical cord delivers oxygen and nutrition to the fetus while removing fetal wast. Wharton’s jelly keeps the umbilical cord from kinking in utero and shortly after delivery of a baby, the jelly solidifies or collapses when it goes from body temperature to room temperature. This change in form clamps the umbilical cord preventing further blood flow between mother and baby. Pretty fascinating tissue when you think about it.
Rich Source of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Let’s compare the number of mesenchymal stem cells found in Wharton’s jelly versus the number of similar stem cells found in bone marrow which has been the traditional source of stem cells. Approximately 1 out of every 10,000 to 1 out every 100,000 cells in bone marrow is a mesenchymal stem cells. One out of every 300 to one out out of every 1,700 cells in Wharton’s jelly is a mesenchymal stem cell.
Other Sources of Stem Cells
- Bone marrow. The stem cells found in the bone marrow are removed by the harvesting process. This means drilling into the bone.
- Lipid (fat) cells found in the adipose tissue of the body. These require removal through liposuction.
- Blood cells. In this case, the extraction is made through apheresis. In this procedure, a certain amount of blood is extracted from the donor, and inserted into a medical machine which removes and separates all the stem cells, while returning some of that blood’s quantity back to the donor.
Properties of Stem Cells
All stem cells, regardless of their source, have three general properties:
- Self-renewal. They are capable of dividing and renewing themselves for long periods. Unlike other types of cells, stem cells can replicate many times, or proliferate. A starting stem population can produce millions of new cells. In the case in which these secondary cells are uncategorized, like the parent stem cells, they can also be capable of long-term self-renewal.
- Stem cells are unspecialized. This is one of the main characteristics of these cells. This mean that it does not have any tissue-specific structures that could allow it to perform specialized functions. For example, a stem cell cannot carry oxygen molecules through bloodstreams.
- Stem cells can produce specialized cells. Even though they are not specialized, stem cells can provide and create specialized cells such as heart muscle, blood cells, or nervous system cells. This process is called differentiation. The cells become more specialized at each step.
Benefits of Wharton’s Jelly MSCs
There are no ethical concerns in using MSCs from Wharton’s jelly (WJ-MSC). The stem cells are obtained through FDA regulated labs in the United States from the tissue from a donor after a scheduled c-section. Normally, the umbilical cord is considered medical waste. But in these cases, the umbilical cord is donated with the mother being consented and undergoing a considerable amount of medical screening beforehand. This is in contrast with ethical issues related to stem cells obtained from aborted fetuses or embryos. .
WJ-MSC are immune privileged meaning they are not likely to cause an allergic or tissue rejection in the recipient. They are also non-tumorigenic unlike embryo stem cells.
As opposed to your own stem cells in your bone marrow and adipose (fat) tissue, MSCs from Wharton’s jelly are young and vibrant. Regardless of your age, your stems cells are older and have fewer growth factors than those obtained from Wharton’s jelly. Here is something amazing. A single MSC from Wharton’s jelly can create up to one billion cells in 30 days as opposed to 200 cells from bone marrow from a 65 year-old.
WJ-MSC contain over 300 growth factors and cytokines compared to 100-200 such molecules found in older stem cells.
WJ-MSCs are harvested by FDA regulated labs. To obtain your own stem cells requires a separate procedure to extract the stem cells from either your bone marrow (not a comfortable procedure) or from you adipose of fat tissue. These procedures to pose additional risks which are avoided by using WJ-MSC.
How WJ-MSC Work
Stem cells from Wharton’s jelly regenerate tissue through several mechanisms.
- Immunomodulatory effects
- Paracrine actions
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Anti-aptosis
- Angiogenesis
WJ-MSC promote good cytokines and interleukins while suppressing harmful ones. This improves our immune’s system to fight disease and infection.
Paracrine refers to cell to cell communication. Stem cells “tell” other cells what to do to promote repair and regeneration.
Chronic inflammation has been shown to be a known precursor to many medical conditions including organ failure, arthritis, several types of cancer and more. Stem cells fight this inflammation.
Apoptosis is programmed cell deaths. Cells are programmed to die after a certain number of divisions which varies among the different cell types.
Anti-apoptosis means prevention of cell death. Basically, WJ-MSC keep cells living longer.
Angiogenesis refers to creation of new blood vessels. Healthy tissues needs blood flow.
For more information on stem cells see our article Stem Cells: What They are and How They Help You.
